⚡ Turbocharge Your Database: How to Identify & Optimize Slow SQL Queries 🚀
⚡ Turbocharge Your Database: How to Identify & Optimize Slow SQL Queries 🚀
Is your application crawling like a snail? 🐌 Chances are, slow SQL queries are the culprit! Poorly optimized queries can cripple your database performance, leading to frustrated users and lost revenue. But fear not! In this guide, we’ll uncover how to find slow queries and supercharge them for maximum efficiency. 💨
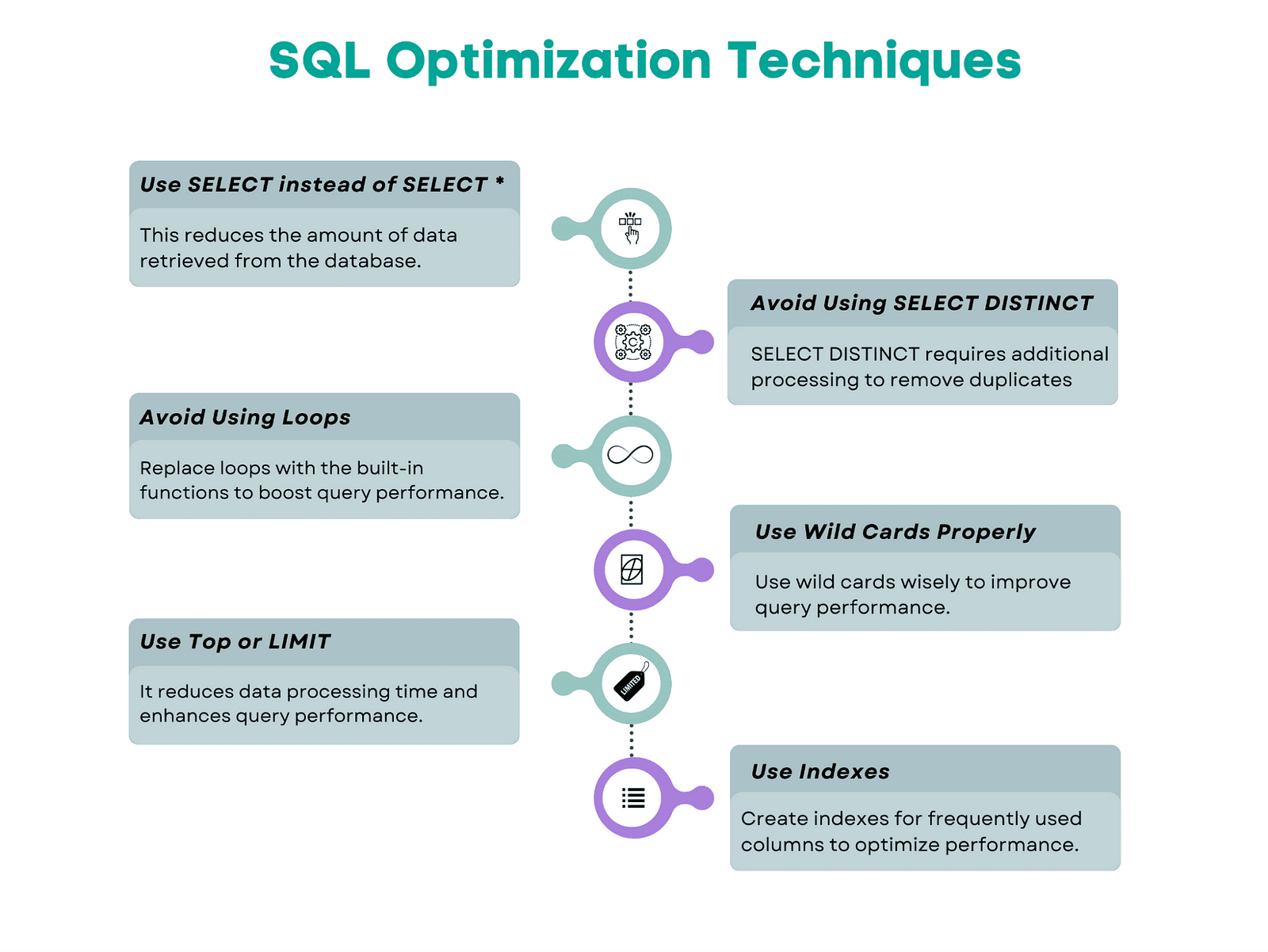
🔍 Step 1: Identify Slow Queries
Before optimizing, you need to know which queries are slowing you down. Here’s how:
1. Database Logging & Slow Query Logs
Most databases (MySQL, PostgreSQL, etc.) have a slow query log feature:
- MySQL:
SET GLOBAL slow_query_log = 'ON'; SET GLOBAL long_query_time = 2; - Log queries slower than 2 seconds- PostgreSQL:
log_min_duration_statement = 2000; - Log queries taking > 2s2. Monitoring Tools
Use tools like:
- EXPLAIN ANALYZE (PostgreSQL)
- MySQL Workbench Performance Dashboard
- Datadog / New Relic (for cloud monitoring)
- pt-query-digest (for MySQL query analysis)
3. Query Execution Time Tracking
Run:
SELECT query, total_time
FROM pg_stat_statements
ORDER BY total_time DESC LIMIT 10; -- PostgreSQL
SELECT * FROM sys.dm_exec_query_stats
ORDER BY total_elapsed_time DESC; -- SQL Server🛠 Step 2: Optimize the Queries
Now, let’s fix those sluggish queries!
1. Use Indexes Wisely 🏎️
Indexes speed up searches but slow down writes.
- Add missing indexes:
CREATE INDEX idx_user_email ON users(email);- Avoid over-indexing (too many indexes hurt INSERT/UPDATE speed).
2. Rewrite Inefficient Queries
- Avoid
SELECT *→ Fetch only needed columns. - Replace
NOT INwithNOT EXISTSorLEFT JOIN + NULL check(faster in many cases). - Use
JOINinstead of subqueries where possible.
3. Optimize JOINs
- Ensure JOIN columns are indexed.
- Reduce the dataset before joining (filter early).
4. Partition Large Tables
Split huge tables into smaller chunks for faster access.
5. Use Query Caching
- MySQL Query Cache:
SET GLOBAL query_cache_size = 1000000;- Application-level caching (Redis, Memcached).
6. Analyze Execution Plans
Use EXPLAIN to see how the database executes your query:
EXPLAIN ANALYZE SELECT * FROM orders WHERE user_id = 100;Look for:
- Full table scans (Seq Scan) → Add an index.
- Poor join strategies → Optimize JOIN conditions.
🚀 Advanced Optimization Hacks
1. Denormalize for Speed
Sometimes, redundant data improves read performance (e.g., storing counts instead of calculating them).
2. Batch Inserts
Instead of:
INSERT INTO users (name) VALUES ('Alice');
INSERT INTO users (name) VALUES ('Bob');Use:
INSERT INTO users (name) VALUES ('Alice'), ('Bob');3. Use Stored Procedures
Reduce network latency by moving logic into the database.
4. Upgrade Hardware
If all else fails, scale vertically (better CPU/RAM) or horizontally (sharding/replicas).
✅ Final Checklist
✔ Log & monitor slow queries.
✔ Use EXPLAIN to analyze bottlenecks.
✔ Optimize with indexes and better SQL.
✔ Cache aggressively.
✔ Consider database tuning & hardware upgrades.
� Conclusion
Slow SQL queries don’t have to be a nightmare! With the right monitoring, indexing, and optimization techniques, you can turn a sluggish database into a speed demon! 🚀
What’s your biggest SQL performance challenge? Drop it in the comments! 💬👇
#SQL #Database #Performance #Optimization #TechTips
Comments
Post a Comment